What desktop UI does Ubuntu 24.04 use?
And why are people still fighting about it in 2026?
If you’ve installed Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Noble Numbat) recently, you might have noticed something: it looks incredibly polished, but also… kinda rigid?
That’s GNOME 46.
On the other side of the fence, you have users posting screenshots of their desktops that look like the flight deck of a spaceship, dripping with blur effects and neon.
That’s usually KDE Plasma.
In this post, I’m digging into why these two desktop environments look so different, the history behind the “war,” and which one actually makes sense for you (or your users).
TL;DR
- Ubuntu 24.04 uses GNOME by default. It’s designed to be an “appliance” – stable, distraction-free, and hard to break.
- KDE Plasma is the “enthusiast” choice (and what the Steam Deck uses). It offers total control and flashy visuals but can be overwhelming.
- The difference isn’t lack of talent; it’s a difference in philosophy (Constraint vs. Agency).
The Philosophy Gap: Appliance vs. Cockpit
The reason the GNOME website (and desktop) looks “boring” compared to KDE’s “amazing” marketing isn’t an accident. It’s a deliberate design choice.
GNOME is an Appliance. Think of it like a microwave or an iPhone. You don’t want to re-wire the control panel of your microwave; you just want to heat your lunch. GNOME follows a philosophy of “Intentional Constraint.”
- They remove settings to prevent you from breaking things.
- They hide complexities to keep you focused on work.
- The Vibe: Minimalist, Zen, Enterprise.
KDE Plasma is a Cockpit. Think of it like a fighter jet or a gaming PC. If you want to move the “Start” button to the top-right corner and make it transparent pink, KDE says, “Go ahead.” It prioritizes “User Agency.”
- They expose every setting imaginable.
- They embrace modern trends like blur, glass, and shadows.
- The Vibe: High-tech, Cyberpunk, Power User.
A Brief History of the Desktop Wars
It wasn’t always just these two. The Linux desktop has gone through several “eras” of dominance.
1. The Golden Age (2002-2008): GNOME 2 Back in the day, GNOME 2 was the king. It was stable, efficient, and everyone loved it. It was the Windows XP of Linux.
2. The Great Schism (2011-2017): Unity & GNOME 3 This is where things got spicy. GNOME 3 launched and radically changed the interface (removing the taskbar, adding the “Activities” overview). Users hated it. Canonical (Ubuntu) famously said “No thanks” and built Unity – their own interface designed for “convergence” (one OS for phone and desktop).
- In my humble opinion: Unity was ahead of its time. The side dock and HUD/glass feel were brilliant, but the community fragmentation was rubbish.
3. The Modern Duopoly (2024-Present) Ubuntu eventually dropped Unity and returned to GNOME, but they heavily customized it (giving us the Ubuntu Dock we have today). Meanwhile, Valve chose KDE Plasma for the Steam Deck, proving that Linux could be a consumer-grade gaming platform.
Which One Should You Choose?
If you are a SysAdmin deploying workstations for 50 employees? Stick with GNOME (Ubuntu Default).
- Why: It’s predictable. You don’t want Bob from Accounting accidentally deleting his taskbar or changing his system font to Wingdings. GNOME is designed to “get out of the way.”
If you are a tinkerer, a gamer, or someone who misses the “Windows XP” layout? Install KDE Plasma (Kubuntu).
- Why: It feels faster (even if it isn’t always) because of the animations. It respects your desire to customise.
How to switch on Ubuntu: If you want to see the difference without reinstalling, just open a terminal:
# To get the KDE FULL experience
sudo apt-get install kubuntu-desktop
# For basic KDE, no presets or tools
sudo apt-get install plasma-desktop --no-install-recommends
# To get the vanilla GNOME experience
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop
# Then to fix it in place reboot to awaken your chosen Desktop Enviroment
sudo rebootThe reality?
Ubuntu uses GNOME because Canonical sells to the Enterprise, and Enterprise loves stability. KDE looks “better” because it’s selling to You, the user.
Personally? I respect GNOME’s discipline, and until recently I ran KDE on my personal rigs when a desktop GUI was needed, simply because I like my buttons exactly where I want them. However I have now grown older and maybe even a tiny bit wiser, and simply go with the flow now, using whatever my distro has selected as the integrated desktop environment for that release.
I have far fewer headaches, and its some extra time saved from customising when really I don’t interact with it all that much (CLI guy & Windows daily driver…).
My honest opinion: If you have time, do what looks best to you, else, stick to defaults.
Defaults are defaults for a reason, and have much better official AND community support.
Posted in: Linux, Ubuntu, Opinion Tagged: GNOME vs KDE, Ubuntu 24.04, Linux Desktop History, Unity Desktop, Noble Numbat
![GNOME VS KDE: THE WAR FOR THE LINUX DESKTOP INTERFACE [ANALYSIS]](https://cannotdisplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/KDE-vs-GNOME-1260x703.png)

![[Opinion] STOP INSTALLING OPENCLAW (MOLTBOT) ON YOUR PC/MAC: How to Safely ‘Hire’ AI Agents via Cloud VPS](https://cannotdisplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/moltbot-banner.png)
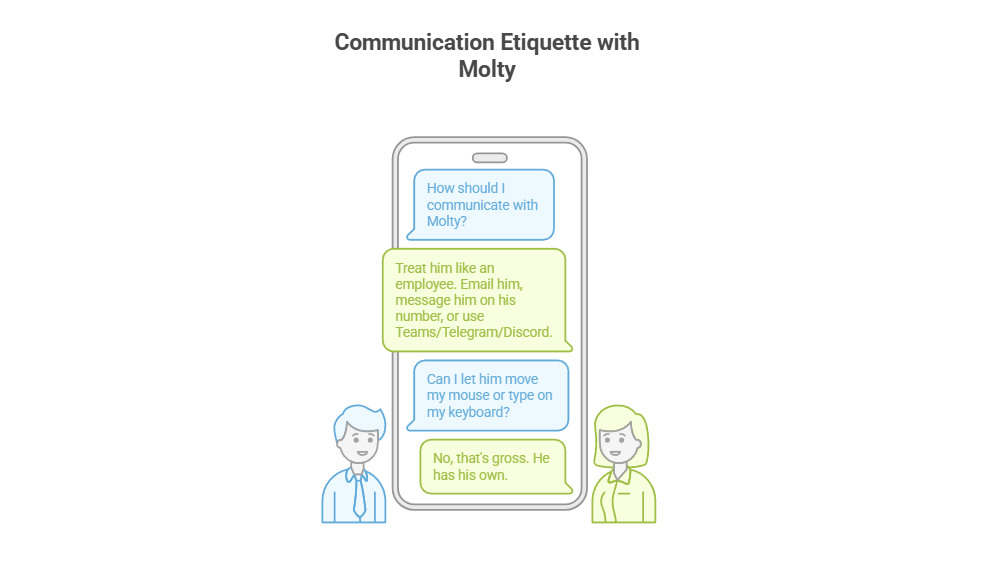
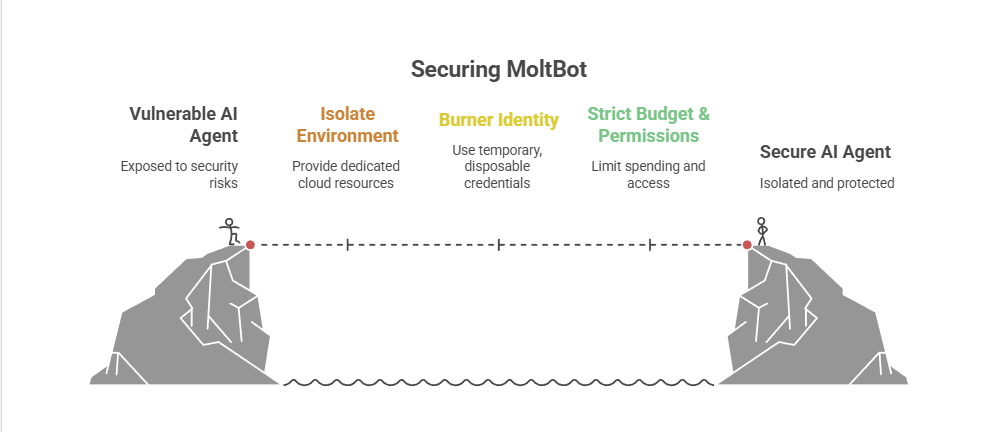
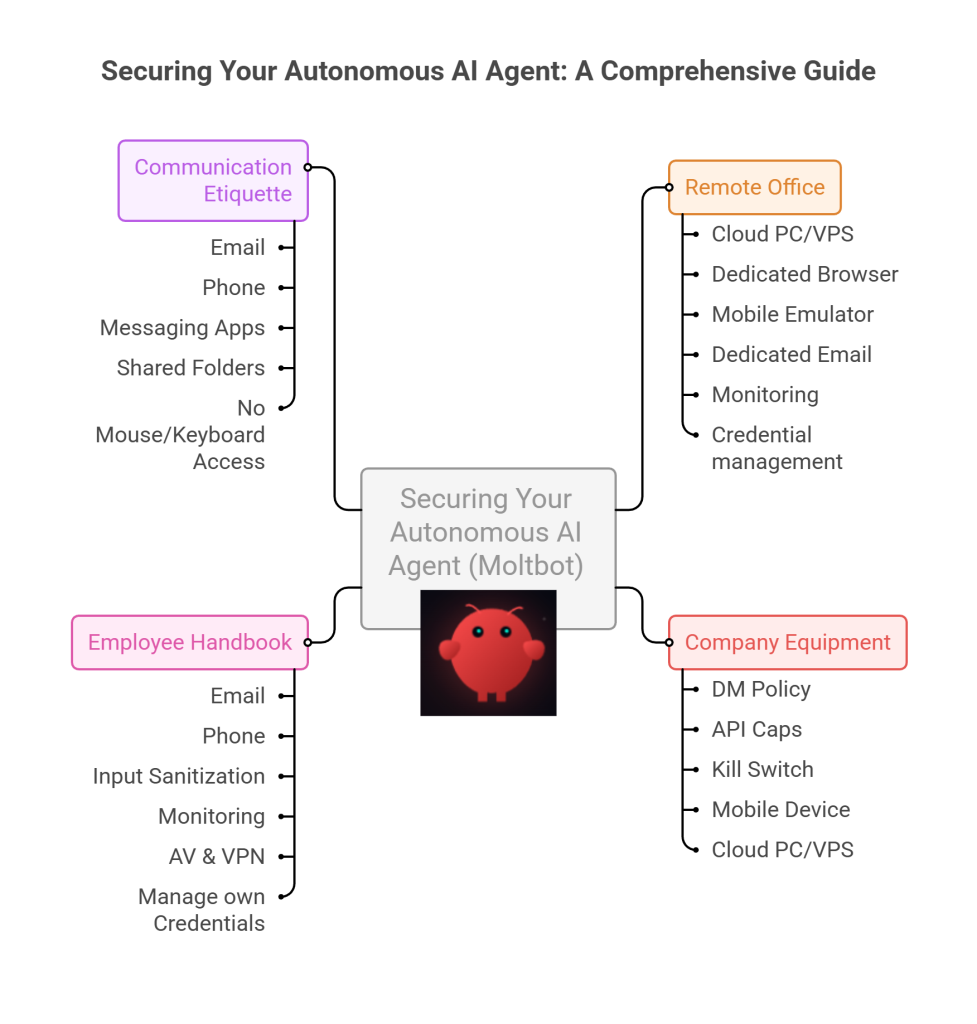
![[Solved] Help! Windows 365 Cloud PC Switch Feature Has Frozen My Local Host PC.](https://cannotdisplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/Win365-Cloud-PC-via-Switch-1260x264.png)
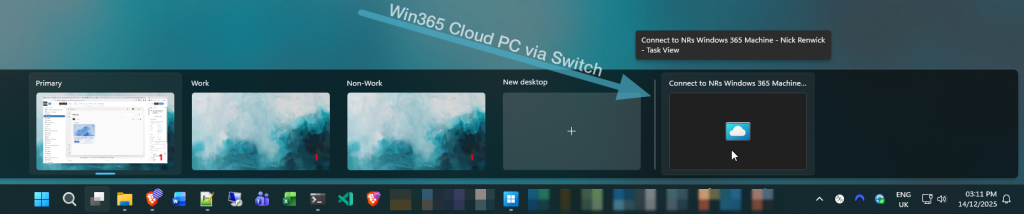
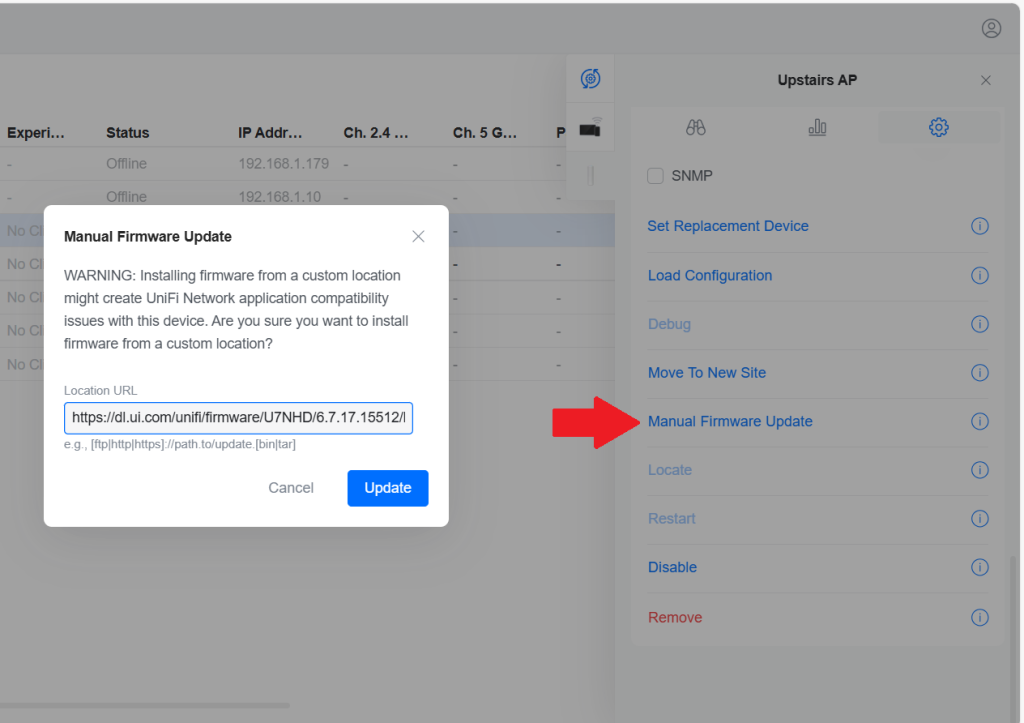
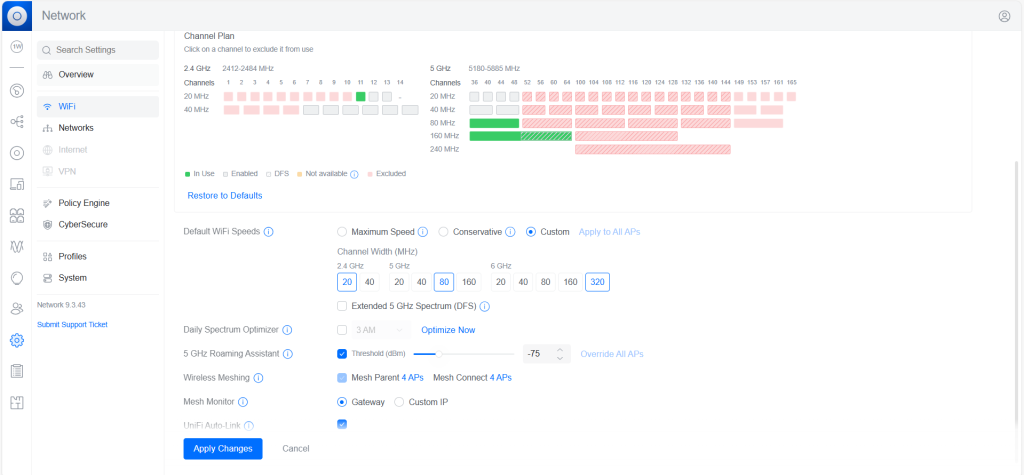
![[SOLVED] UniFi AP Firmware 6.7.31: Breaking Wireless Meshing and Causing Channel Hopping – Here’s the Fix.](https://cannotdisplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Unifi6.7.3.1BreakingUpdate.png)

![[SOLVED] How to insert todays time or date automatically *anywhere* into an Excel spreadsheet](https://cannotdisplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/solved-excel-date-time-shortcut.png)