There are many reasons you may wish to change the RDP port on a RDS or terminal services server.
My default action when setting up a new RDS server is now to ensure that it is not listening on the standard port (3389). This is for multiple reasons, mainly though to add a small extra layer of protection against automated RDP bruteforce attacks. Sure if an attacker wanted to they could run a port scan to find the new port, but really unless you are targeted, no-one is going to do this via bot/automation.
The easiest way to change the RDP port is via regedit:
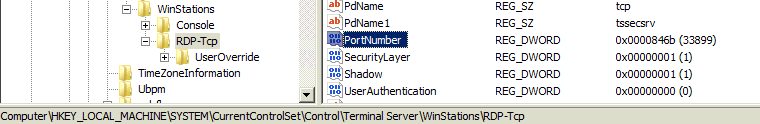
Navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\
and change the value of the DWORD "PortNumber" select Decimal and change to whatever you wish the port to be.
You will then need to restart the server for this to take effect – simply restarting the gateway services does not seem to refresh the listening port.
Other option is to put this into a .reg file and simply click on it to merge the rdp port change into the registry. To do this, copy the below script into notepad and save it is a .reg file:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp]
"PortNumber"=dword:0000846c
This will change the port to 33899